Partial 2.
QUANTIFIERS
We use the quantifiers much, many, a lot of, lots of to talk about quantities, amounts and degree. We can use them with a noun (as a determiner) or without a noun (as a pronoun).

Activity 1:
Exercise 1
Revise this video and the presentation available in schoology: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FtruQRWZ44U
Exercise 2
Go into e-zone and log in your username and password available in schoology called

Activity 1:
Exercise 1
Revise this video and the presentation available in schoology: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FtruQRWZ44U
Exercise 2
Go into e-zone and log in your username and password available in schoology called
e_zone_codes.pdf
Into the course FOR REAL BEGINNER
Push start and in cyberhomework push do it. (for everybody just the first activity)
Exercise 3
Then Do the quiz "countable and uncountable nouns" in schoology

Download the worksheet available in schoology and watch the video to answer it.
Exercise 3
For the ones who don't have workbook go to e-zone and do the assignation Module 6- Unit 12- Homework 1 and 2.
Activity 5.
COMPARATIVES AND SUPERLATIVES

Comparative adjectives are used to compare differences between the two objects they modify (larger, smaller, faster, higher).
Activity 2:
Superlative adjectives are used to describe an object which is at the upper or lower limit of a quality (the tallest, the smallest, the fastest, the highest). They are used in sentences where a subject is compared to a group of objects.
Activity 3:
Exercise 1
Go to this link: https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/english-grammar-reference/comparative-and-superlative-adjectives , revise the rules for comparative and superlative adjectives and practice doing the activities there - Comparative adjectives 1-2
- Superlative adjectives 1-2
- How to form comparative and superlative adjectives.
Exercise 2
Continue working in Gateway workbook unit 9 ,100% each activity.Exercise 3
For the ones who don't have workbook go to e-zone and do the assignation Module 6- Unit 12- Homework 1 and 2.
Activity 4:
Participate in the discussion topic " Life in the Capital" available in schoology. Don't forget to use comparative and superlative statements.

There are four demostratives in English: the "near" demostratives this and these, and the "far" demostratives that and those. This and that are singular; these and those are plural.

Participate in the discussion topic " Life in the Capital" available in schoology. Don't forget to use comparative and superlative statements.

DEMOSTRATIVES.
The Demostratives are mostly used to specify or identify people, animals or things based on their proximity or distance, taking into account the position of the speaker.There are four demostratives in English: the "near" demostratives this and these, and the "far" demostratives that and those. This and that are singular; these and those are plural.

Go to schology and do the quiz about demostratives.
SHOULD, MUST, HAVE TO

People use should or shouldn’t to give an opinion about what the best thing to do is. When we speak to another person our opinion becomes advice.


We use must or have to to explain that something is necessary.
- I must finish my homework before 8:00
- I have to phone Valery before 9:00
a. We use have to when the situation makes something necessary, for example because of official rules. The speaker in here expresses facts, not his/her own feelings.

Examples:
- At our school, we have to wear a uniform
- To board the suburban train, we have to use a special card
- To take an examination, students have to be in the classroom on time
b. We use must when the speaker personally feels that something is important. She/he is saying what she/he thinks is necessary.

Examples:
- You really must stop working so hard and go on vacation
- We must be here by 8:00 or the plane will leave without us
- She must stop eating junk food or she'll get fatter!
a. Mustn't describes an action that is prohibited / forbidden.
- You mustn’t turn on your cell phone when the plane is taking off
- You mustn't combine sleeping pills with alcohol. It’s dangerous!
- You don't have to turn on the heating system. It´s automatic.
Activity 6:
Go into this link https://www.eslgamesplus.com/body-parts-board-game-for-esl-practice/ and revise parts of the body.
Go into this link https://www.eslgamesplus.com/body-parts-board-game-for-esl-practice/ and revise parts of the body.
Activity 7:
Go into this link https://matchthememory.com/suly to revise illnesses.
Activity 8:
Go into this link https://www.eslgamesplus.com/modal-verb-should-shouldnt-for-giving-advice-on-health-problems-esl-grammar-activity/ to revise health problems.Final Activity
Finally, go into schoology and do the final quiz for revising all the topics seen in the second partial.

KEEP IN TOUCH!
WE HAVE NOT FINISHED YET.
Partial 3.
SIMPLE PAST VERB TO BE.
How old were you last year?
Where were you yesterday evening?
What was the weather like yesterday?
To answer similar questions we need to use the verb To Be in past.
Using verb To Be in past (was /were) , we can formulate affirmative, negative and interrogative sentences in order to ask for or give information. Now, we are going to study the general characteristics of three forms:
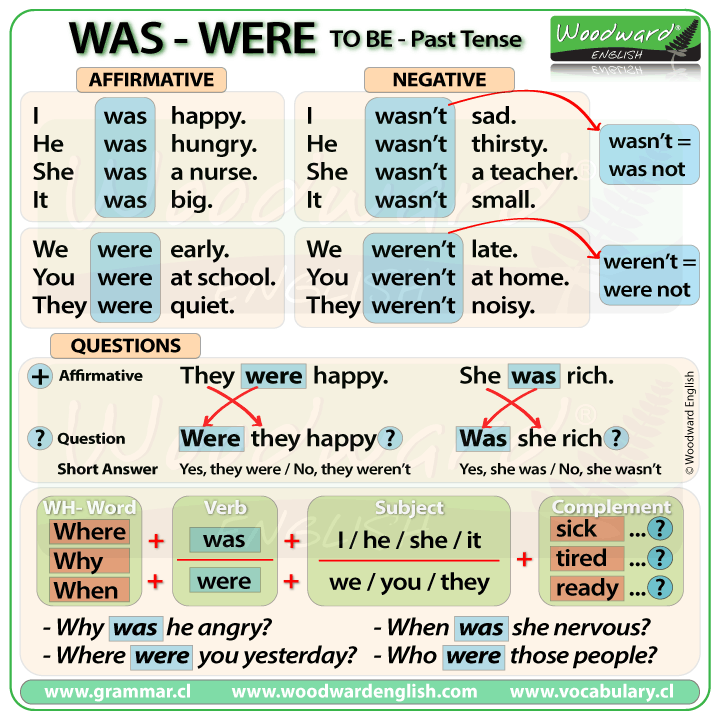
If you can see in the paragraph below, we are describing a person, her nationality, her origin, her age when she wrote the song, her profession and more information about her using was, this is the past tense of To be.
As mentioned above, we sometimes use were but we can also use was, all depends on the subject. In the following explanation we will learn how to use each one.

Activity 1: ( From April 27th to May 1st)
Go into schoology and do the activities available in "Verb to be in PAST"
Exercise 1:


Read the text about Pedro Infante's life and answer the questions.
Exercise 2:


Watch the video about the Beatles and answer true and false statements.
Activity 2:

Write about the most memorable concert or even you have been using was / were.Activity 2:

Activity 3: (Date of delivery: May 15th)
Workbook Gateway unit 7 for the ones who have the WB and Ezone assignation U13_HW1/2 for the ones who don't have workbook.
You can find several past phrases to express when the things or activities happened. Here you can see some of them.
SIMPLE PAST REGULAR VERBS.
The simple past is a verb tense which is used to show that a completed action took place at a specific time in the past.You can find several past phrases to express when the things or activities happened. Here you can see some of them.
You need to see the structure of the affirmative sentences in past. The past phrases can be at the beginning or the end of the sentence when necessary.

In this tense, you can use two types of verbs regular and irregular. With regular actions, you may see a particular characteristic that is the “ed” ending.

1. Verbs in infinitive that end with “t” or “d” You pronounce the “ed” ending as /Id/
Examples:
visit → visited (visit/Id/)
need → needed (need/Id/)
2. Actions that are voiced sound ( n, l, m, f, v, r, vowels ) considering the last consonant(s) in the infinitive form. You pronounce the “ed” ending as /d/
Examples:
arrive → arrived (arriv/d/)
email → emailed (email/d/)
3. Verbs that are voiceless (k, p, s, sh, ch, x) sound taking into account the las consonant(s) in the infinitive form. You pronounce the “ed” ending as /t/
Examples:
like → liked (lik/t/)
wash → washed (wash/t/)
Affirmative:

Pronuntiation of the "ed" ending.
There are three different forms to articulate this ending.1. Verbs in infinitive that end with “t” or “d” You pronounce the “ed” ending as /Id/
Examples:
visit → visited (visit/Id/)
need → needed (need/Id/)
2. Actions that are voiced sound ( n, l, m, f, v, r, vowels ) considering the last consonant(s) in the infinitive form. You pronounce the “ed” ending as /d/
Examples:
arrive → arrived (arriv/d/)
email → emailed (email/d/)
3. Verbs that are voiceless (k, p, s, sh, ch, x) sound taking into account the las consonant(s) in the infinitive form. You pronounce the “ed” ending as /t/
Examples:
like → liked (lik/t/)
wash → washed (wash/t/)
Sentences.
- Subject + verb in past “ed” ending + complement
- Yesterday I cooked a delicious meal.
- On Wednesday morning you printed a poster.
- Salma Hayek moved to the U.S.A.
- Mexican students finished their courses in Europe five months ago.
Negative:
- Subject + didn't + infinitive verb + complement
- Yesterday I didn't cook a delicious meal.
- On Wednesday morning you didn't print a poster.
- Salma Hayek didn't move to the U.S.A.
- Mexican students didn't finish their courses in Europe five months ago.
Interrogative:
- Did + Subject + infinitive verb + complement ?
- Did I cook a delicious meal yesterday ?
- Did you print a poster on Wednesday morning ?
- Did Salma Hayek move to the U.S.A ?
- Did Mexican students finish their courses in Europe five months ago ?
( From May 3rd to May 7th)
Activity 1:
Go into this link https://www.quia.com/cb/25733.html and practice rules for regular verbs.
Activity 2:
Go into schoology and do the quiz "Past events"
Activity 3:
Assignation U14_HW 1 on Ezone for those who don't have workbook.
Go into schoology and do the quiz "Past events"
Activity 3:
Assignation U14_HW 1 on Ezone for those who don't have workbook.
( From May 18th to May 22nd)
SIMPLE PAST IRREGULAR VERBS
think - thought
see - saw
write - wrote
say - said
draw - drew
do - did
As you could notice in this case their ending is different and there is no rule, for this reason you need to learn them by heart. In this link you can find more examples:


When we ask for specific information we use wh-question words at the beginning:
Examples:
What did you wear for the party?
I wore a beautiful red dress and high heels.
How did you know you were soul mates?
I don’t know, but when I met him I just felt it.
When did you have your first kiss?
Oh, when I was 15 years old.
Where did you celebrate Christmas last year?
I celebrated Christmas at my mom’s home.
Why did you react like that?
Because I was in love with her.
Review Irregular Verbs in the Past Simple in the Interactive Grammar Hangman Spelling Game Online https://www.eslgamesplus.com/irregular-verbs-interactive-hangman-game-for-esl-grammar/ and upload the final score in schoology into a screenshot or photo.
Activity 8:
Go into Past Simple Snakes & Ladders and answer each question to get a chance at rolling the dice
http://www.eslgamesworld.com/members/games/grammar/New_Snakes_%20Ladders/Past_simple_tense.html . Upload the final score in schoology into a screenshot or photo.
Activity 9.
Go into https://www.gamestolearnenglish.com/past-tense-game/ and . Don't forget to register your Name and Location so that your score appears in the list. Finally upload the final score into a screenshot.
Activity 10:
Workbook Gateway unit 8 for the ones who have the WB and Ezone assignation U14_HW2 for the ones who don't have workbook.
USES OF SIMPLE PAST TENSE.
USE 1 Completed Action in the Past

Use the simple past to express the idea that an action started and finished at a specific time in the past. Sometimes, the speaker may not actually mention the specific time, but they do have one specific time in mind.
Example:
I saw a movie yesterday.
USE 2 A Series of Completed Actions

We use the simple past to list a series of completed actions in the past. These actions happen 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and so on.
Example:
I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim.
USE 3 Duration in the Past

The simple past can be used with a duration which starts and stops in the past. A duration is a longer action often indicated by expressions such as: for two years, for five minutes, all day, all year, etc.
Example:
I lived in Brazil for two years.
USE 4 Habits in the Past

The simple past can also be used to describe a habit which stopped in the past. It can have the same meaning as "used to." To make it clear that we are talking about a habit, we often add expressions such as: always, often, usually, never, when I was a child, when I was younger, etc.
Example:
They never went to school, they always skipped class.USE 5 Past Facts or Generalizations

The simple past can also be used to describe past facts or generalizations which are no longer true. As in USE 4 above, this use of the simple past is quite similar to the expression "used to."
Example:
She was shy as a child, but now she is very outgoing.
Example:
She was shy as a child, but now she is very outgoing.
teacher
ResponderEliminarShould I register at this link?
https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/english-grammar-reference/comparative-and-superlative-adjectives